HiveOS Manual Installation: CUDA
You must have an instance of the quai stratum proxy before running a GPU miner.
Introduction
Here, we'll be installing quai-gpu-miner, the main implementation of a Quai Network GPU miner.
This tutorial focuses on installing and running quai-gpu-miner on HiveOS, a Linux based operating system that makes GPU mining easy. HiveOS also provides a web based dashboard for streamlined management and maintenance of your Quai Network GPU miner.
If you are mining for Testnet Rewards, be sure to KEEP THE PRIVATE KEYS OF THE ACCOUNTS YOU MINE INTO. Signing transactions from the accounts you mine into (using their private keys) will be the only acceptable way to prove how many blocks you mined in the Iron Age Testnet when it is time to claim Mainnet rewards.
Requirements
In order to run the quai-gpu-miner on HiveOS and mine valid blocks, you'll need the following:
- A synced go-quai node
- A stratum proxy connected to your go-quai node
- A machine running HiveOS with:
- At least one AMD or Nvidia GPU
- An AMD or Intel CPU
- 4GB+ of RAM
Common Troubleshooting Resources
- How to find the IP of a Stratum Proxy
- "No usable mining devices found" error
- "SIGSEGV encountered" error
- Low hashrate on AMD cards
- Error on make and/or build step
Additional troubleshooting resources are available in the GPU Miner FAQ.
Environment Setup
HiveOS
To run the quai-gpu-miner, you'll first need to install and configure HiveOS. Instructions on how to install HiveOS on your rig and configure it can be found on the HiveOS install documentation.
Installing Without Script
The recommended method of installing and building the miner in HiveOS is with the provided script. The manual installation is only recommended for users needing more customization regarding drivers/packages.
Drivers and Updates
Once you've installed and set up HiveOS on your rig, you'll need to update drivers, install some GPU utility packages, and ensure Hive is up to date.
Prior to starting updates and installs, we need to switch users. Do this by running:
sudo su user
To upgrade HiveOS, run:
sudo selfupgrade
To update and install necessary graphics card drivers, run:
sudo nvidia-driver-update
Dependencies
Prior to installing any dependencies, you'll first want to make sure the system is up to date. We can do this by running:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
After Ubuntu has updated, we can begin installing the following dependencies:
gitcmakebuild-essentialmesa-common-dev- Nvidia CUDA Toolkit v12.1
Install dependencies using the following command:
sudo apt install -y git cmake build-essential mesa-common-dev
Finally, after installing all necessary dependencies and drivers, reboot your machine to ensure all updates are applied correctly using:
Install CUDA with the following commands:
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.1.0/local_installers/cuda_12.1.0_530.30.02_linux.run
sudo sh cuda_12.1.0_530.30.02_linux.run
The above command will open a flow where you are able to select which components of the CUDA Toolkit you'd like to install. Ensure your selections are IDENTICAL to the image below.
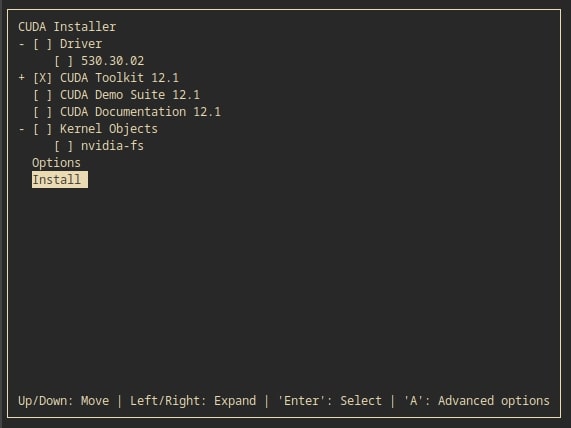
Unselect "Driver", and only select "CUDA Toolkit 12.1".
After completing this step, you may see a warning saying that the CUDA compatible drivers were not installed -- as long as you previously ran nvidia-driver-update, you can safely ignore this warning.
sreboot
Configure and Run
Now that the environment and dependencies are fully configured, we can start installing quai-gpu-miner.
First, make sure you're in the home directory for the correct user. You can do this by running:
sudo su user -
Now, clone the quai-gpu-miner and navigate to the quai-gpu-miner directory:
git clone https://github.com/dominant-strategies/quai-gpu-miner && cd quai-gpu-miner
To install and update external repository dependencies, run the following:
git submodule update --init --recursive
This will ensure that all the submodules referenced in the repository are properly initialized and up to date.
Build
Start by making a directory named build and navigating to it:
mkdir build && cd build
Inside of the build directory, we'll need to install all of the build dependencies using cmake and then build and compile the miner:
cmake .. -DETHASHCUDA=ON && cmake --build .
Running this command may take a while to complete, and will require about 10gb of RAM. If you don't have enough RAM on your rig to compile, some users have had success compiling on a different machine and sending the compiled binary to the rig.
Configure and Run
Run
To run the miner, you'll need a quai-stratum-proxy to connect to. Visit the quai-stratum-proxy docs for information on how to install and configure it. The proxy configuration will determine which shard your gpu-miner is running on and the address payouts are awarded to.
First, you'll need to obtain the IP Address and port your proxy is running on. The default port is 3333.
Once you have the address and port and are in the build directory, run the following command to start the miner:
Replace PROXYIPADDRESS with the IP address of your proxy. Replace STRATUMPORT with the websocket port of your proxy, which is default set to 3333. Note that when using CUDA, the start command utilizes a -U flag instead of a -G flag.
./ethcoreminer/ethcoreminer -U -P stratum://PROXYIPADDRESS:STRATUMPORT
The quai-gpu-miner should now be running and outputting logs to the terminal. Now that your miner is running, learn how to optimize your miner in the FAQ!
When running on HiveOS, you can use a community-built flight sheet to easily manage your rig(s). Learn how to configure and use the flight sheet in the GPU miner FAQ.
Do not start the miner before confirming your node has fully synced. Mining while your node is not synced will result in the mining of invalid blocks and wasted hash.
Stop
To stop the miner, simple use CTRL+C to kill the terminal process. Once logs are no longer being outputted to the terminal, the miner has stopped.